This post explains how to set up basic monitoring with Prometheus of the Docker environment running on your developer machine.
Pometheus - From metrics to insight
In this walk-through we essentially follow the instructions from docker docs - Collect Docker metrics with Prometheus while developing a reusable Docker Compose setup.
Find the location of your Docker system’s daemon.json.
If unsure check the section Configure Docker in Collect Docker metrics with Prometheus.
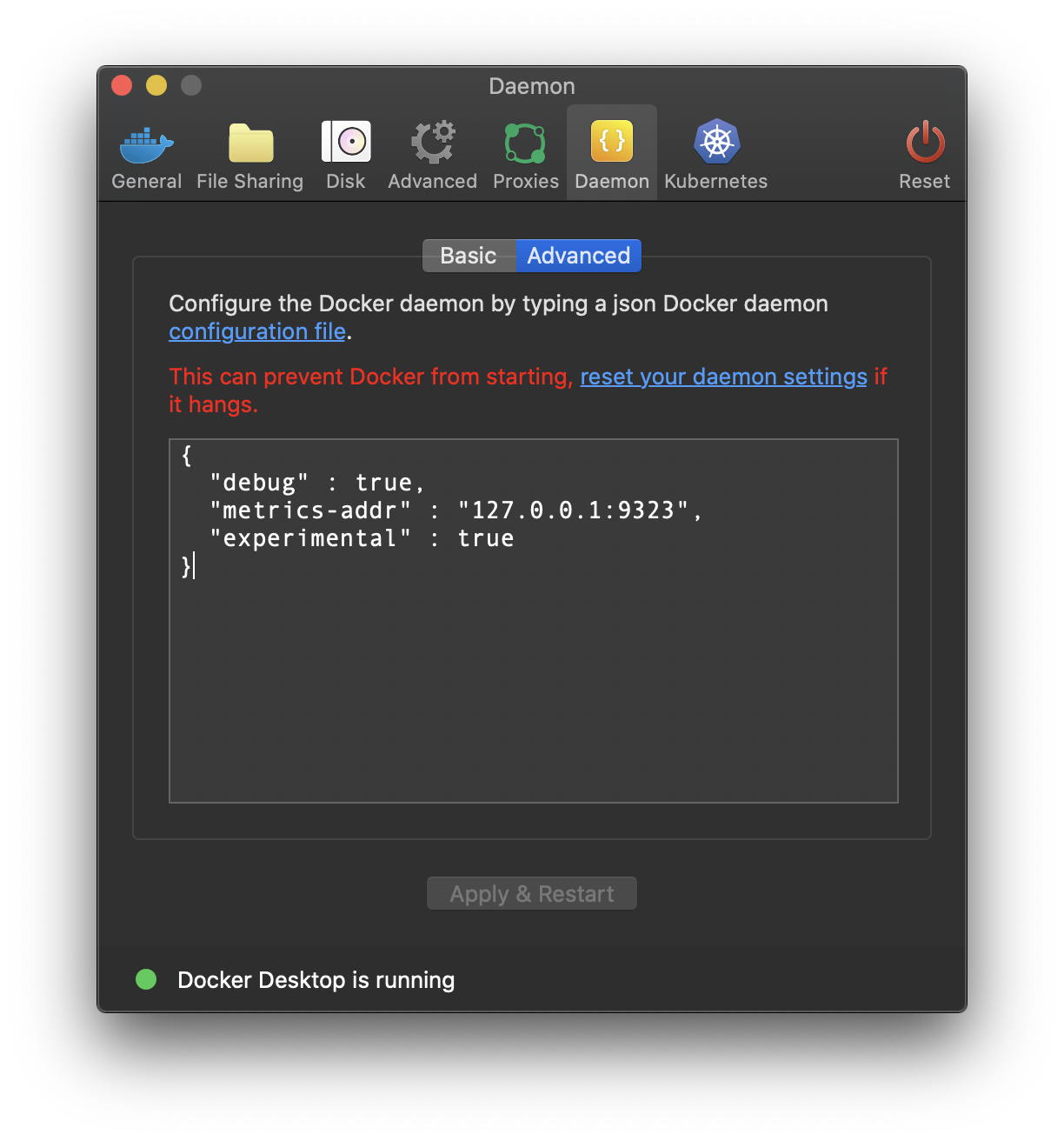
{
"metrics-addr" : "127.0.0.1:9323",
"experimental" : true
}
Note: Such a configuration change requires a restart of the Docker daemon.
Whether the Docker metrics are available or not can be verified with a simple get request (e.g. via browser) to the URL http://localhost:9323/metrics
Prepare a small docker-compose.yaml for the Prometheus service.
version: "3.7"
services:
prometheus:
image: prom/prometheus:v2.15.2
volumes:
- ./prometheus/prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
command:
- '--config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml'
ports:
- 9090:9090
Hint: You might want to check for the latest available version on DockerHub prom/prometheus.
Put the minimal configuration file prometheus.yml into a subfolder named prometheus.
global:
scrape_interval: 15s
scrape_timeout: 10s
evaluation_interval: 15s
external_labels:
monitor: codelab-monitor
scrape_configs:
- job_name: docker
honor_timestamps: true
scrape_interval: 15s
scrape_timeout: 10s
metrics_path: /metrics
scheme: http
static_configs:
- targets:
- docker.for.mac.host.internal:9323
Fire up the Prometheus container and check the results/targets http://localhost:9090/targets/
Congratulations you’ve successfully set up a monitoring for your local Docker environment! 👏